Week-1 (Database Systems Intro)
CE208-Database Management Systems¶
Week-1 (Intro)¶
Spring Semester, 2021-2022¶
Instructor: Yıldıran Yılmaz Email: yildiran.yilmaz@erdogan.edu.tr Office Hours: Thursday
Download PDF-MS, PDF-MD, DOCX-MD, PPTX-MD, PPTX-MS
Outline¶
- What is Database?
- Database Examples
- Database
- What is Database Management System?
- Classification of Database Management Systems
Outline¶
- Hierarchical databases
- Network databases
- Relational databases
- Object Oriented databases
- Why use a database?
- Advantages of the Database Approach
- Database Management Systems
Outline¶
- Database Structure
- Table
- Data Types
- MYSQL Data Types
- Key
- Primary key
- Foreign key
- Database Design
What is Database?¶
-
It is an information repository where data that is related to each other is kept.
-
The collection of data arranged in accordance with the purpose of use
-
They are information stores with their logical and physical definitions.
Database Examples¶
-
University - Student Affairs Information System
-
Hospital - Patient, doctor, treatment, equipment, financial information
-
A commercial company - Customer, Product, Sales, Payment, Delivery information
-
Bank - Customer, deposit, credit card, credit information
Database¶
-
The database concept was first introduced in the 1980s.
-
It is used in everywhere from a simple web application up to large and complex data of international organizations
-
Database applications are needed in many areas.
What is Database Management System?¶
It is a software system in which various complex following operations are performed.
- Creating a new database,
- Editing the database
- To use,
- Develop
- to take care of (maintanance)
Classification of Database Management Systems¶
- By Data Model
- Hierarchical
- Network
- relational
- Object Oriented
- By Number of Users
- single user
- multi-user
Hierarchical databases¶
-
It is the first model used for databases.
-
Hierarchical databases store information in a tree structure.
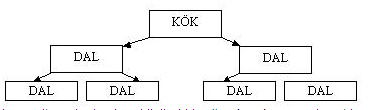
Network databases¶
- When hierarchical databases were insufficient, a structure in which data was stored in the form of graphs, which is a more advanced version of trees, emerged at the end of the 1960s.
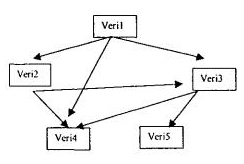
Relational databases¶
-
It was developed in the early 1970s.
-
In this system, data is stored in tabular form.
-
Connections between tables are represented by mathematical relationships.
-
Almost all database programs today have this structure.
Relational databases¶
Object Oriented databases¶
-
Objects used in many word processor and spreadsheet programs today are also used in databases.
-
Object-oriented database means a database created and used in an object-oriented language such as
C++,C#,java,Visual Basic.
Why use a database?¶
-
The traditional approach to holding, storing and accessing data uses the approach of grouping data into separate files.
-
With the increase in data and the need to access and edit data at the same time, the traditional approach has been inadequate.
Advantages of the Database Approach¶
-
Preventing duplication of common data;
-
Ensuring centralized control and consistency of data
-
Ensuring data sharing
-
Hiding physical structure and access method complexities from the user with multi-layered architectures,
-
Presenting only the data that is of interest to each user in easy, understandable structures
Advantages of the Database Approach¶
-
Ease of application software development with the analysis, design and development tools provided.
-
Providing the necessary facilities for data integrity,
-
Ensuring the desired level of security and confidentiality
-
Solving operational problems such as backup, reboot, repair
Database Management Systems¶
-
Oracle database
-
IBM DB/2
-
Adaptive Server Enterprise
-
Informix
-
Microsoft Access
-
Microsoft SQL Server
-
Microsoft Visual FoxPro
-
MySQL
Database Management Systems¶
-
PostgreSQL
-
Progress
-
SQLite
-
Teradata
-
CSQL
-
OpenLink Virtuoso
Database Structure¶
Table¶
- A database consists of data stored in tables.
- Tables are a group of data that is formed by arranging data in rows and columns.
- For example, 2 tables are created to store the course content and student information in the database:
- Student information
- contents
Table¶
-
Each piece of information in the table is called a record , and the columns are called a field .
-
For example, in the student information table, following information is included.
- Student number,
- Name and surname,
- date of birth,
- Place of birth,
- E mail address
Table¶
| Ogr_no | Ad_soyad | d_tarih | d_yeri | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ayşe Öztürk | 01.11.1979 | Konya | ayse@gazi.edu.tr |
| 2 | Sema Özdemir | 24.05.1975 | Ankara | sema@gazi.edu.tr |
| 3 | Serdar Gülpınar | 06.06.1983 | Adana | serdar@gazi.edu.tr |
| 4 | Mehmet Efe | 11.02.1978 | Niğde | mehmet@gazi.edu.tr |
| 5 | Zerrin Polat | 22.08.1980 | Antalya | zerrin@gazi.edu.tr |
| 6 | Ulviye Kubalı | 12.12.1984 | İstanbul | ulviye@gazi.edu.tr |
Table¶
Fields
| Ogr_no | Ad_soyad | d_tarih | d_yeri | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Record
| 1 | Ayşe Öztürk | 01.11.1979 | Konya | ayse@gazi.edu.tr |
| 2 | Sema Özdemir | 24.05.1975 | Ankara | sema@gazi.edu.tr |
Data Types¶
-
In order to have information about the structure of the records kept in the database, some properties of the fields must be defined beforehand.
-
For example, the personnel registration number must be made up of integers, names and surnames must be words.
MYSQL Data Types¶
-
Numeric
-
Date and Time
-
Textual (String)
-
Spatial
MYSQL Data Types¶
TINYINT :¶
- For very small integer values
- When Signed is defined, the values are between
-128and127. - Unsigned defined range is between
0and255.
MYSQL Data Types¶
SMALLINT :¶
- For small integer values
- When Signed is defined, the values are between
-32768and 32767. - Unsigned defined range is
0to65535.
MYSQL Data Types¶
MEDIUMINT :¶
-
For medium-sized integer values.
-
When Signed is defined, the values are between
-8388608and8388607. -
Unsigned defined range is between 0 and
16777215.
MYSQL Data Types¶
INT(n):Interger¶
-
For normal-sized integer values.
-
When Signed is defined, the values are between
-2147483648and2147483647. -
Unsigned defined range is between
0and4294967295.
MYSQL Data Types¶
BIGINT :¶
- For large integer values.
- Can take integer value
-9223372036854775808to9223372036854775807
MYSQL Data Types¶
FLOAT :¶
-
Keeps numbers with their fractions.
-
Max. character width is taken as a parameter. (
up to 23 digits)
MYSQL Data Types¶
DOUBLE:¶
-
Keeps numbers with their fractions.
-
Max. character width is taken as a parameter. (
24 to 53 digits)
MYSQL Data Types¶
DECIMAL:¶
-
Keeps numbers with their fractions.
-
The integer part can have a maximum
64 digits, and the fractional part a maximum30 digits.
MYSQL Data Types¶
DATETIME:¶
- Datetime information in
Year+Month+Day+Hour+Minute+Secondformat
MYSQL Data Types¶
TIMESTAMP:¶
- Time information from
January 1, 1970toJanuary 18, 2038, in the formatYear+Month+Day+Hour+Minute+Second.
MYSQL Data Types¶
DATE:¶
- Date field that can change from
1000-01-01to9999-12-31.
MYSQL Data Types¶
CHAR(n):¶
- Fixed-length data with n characters.
MYSQL Data Types¶
TEXT:¶
- A text field that can hold up to
65535characters.
MYSQL Data Types¶
MEDIUMTEXT:¶
- Text field up to
16777215characters
MYSQL Data Types¶
VARCHAR(n):¶
- Characters of varying size, not exceeding n
MYSQL Data Types¶
BOOL:¶
- A data type that takes the value
0or1. orTrue/ False
Key¶
- A key forces one or more fields to be entered as qualifiers for a row.
- There are 2 types of keys:
- Primary Key
- Foreign Key
Primary key¶
-
It is the key data that will enable access to a record.
-
For example, there are two Ahmet among the students. Each student must have a unique number in order to find the Ahmet we want while searching.
-
For example student number could be a primary key
-
Multiple fields can have primary keys together
Foreign key¶
- A foreign key is a set of attributes in a table that refers to the primary key of another table. The foreign key links these two tables.
Foreign key¶
Persons Table
| PersonID | LastName | FirstName | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hansen | Ola | 30 |
| 2 | Svendson | Tove | 23 |
| 3 | Pettersen | Kari | 20 |
Foreign key¶
Orders Table
| OrderID | OrderNumber | PersonID |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77895 | 3 |
| 2 | 44678 | 3 |
| 3 | 22456 | 2 |
| 4 | 24562 | 1 |
Foreign key¶
-
Notice that the "PersonID" column in the "Orders" table points to the "PersonID" column in the "Persons" table.
-
The "PersonID" column in the "Persons" table is the PRIMARY KEY in the "Persons" table.
-
The "PersonID" column in the "Orders" table is a FOREIGN KEY in the "Orders" table.
-
The FOREIGN KEY constraint prevents invalid data from being inserted into the foreign key column, because it has to be one of he values contained in the parent table.
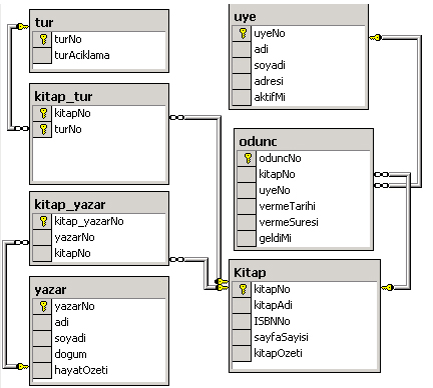
Database Design¶
-
Objects are defined
-
Library system: books, members, types, loan movements
Designing a database¶
- A table is created for each object:
-
book,
-
members,
-
types,
-
woodc_movements
Designing a database¶
-
A key field is selected for each table
-
book table: book no
-
Members table: Userno
Designing a database¶
-
A column is added to the table for each property of the objects
-
Book table: book number, year, author, name, related field
Designing a database¶
- Additional tables are created for recurring object properties.
- request table:
| userno | request_date | Book_name | Book_date | Book_author | Related_field |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
Designing a database¶
- Fields that are not directly related to the table are determined.
-
The address of the member who borrowed the book in the loan transactions table is not directly related to this table.
-
This data should be included in the members table where member information is kept.
Designing a database¶
- Relationships between tables should be defined.
- The relationship between the fields in a table is defined.
- For example, the userno field in the members table should be associated with the userno field in the request table.
Resources¶
-
Köseoğlu, K. (2005). Veri Tabanı Mantığı. Şefik Matbaası. İstanbul
-
Alokoç Burma, Z. (2005). Veritabanı Yönetim Sistemleri ve SQL / PL - SQL / T – SQL. Seçkin Yayıncılık. Ankara
\(End-Of-Week-1-Module\)